

The most common precipitating factor for MH is the use of volatile anaesthetic agents, such as succinylcholine. Clinical Relevance - Malignant Hyperthermia In this article, we will look at the structure and function of the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and consider some clinical relevance. The endoplasmic reticulum is classified as either rough or smooth, with minor variations in size and function in specialised tissue. Its physiological function has a very close association with that of the Golgi apparatus and together, they form the secretory pathway of the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is the major site of synthesis in the cell. It is a system of flattened sacs (cisternae) that are continuous with the outer nuclear envelope. Dantrolene works by inhibiting release of Ca 2+ from the SR. Muscle relaxants – dantrolene and discontinuation of the trigger are the treatments of choice.

Systemic effects as a result of acidosis can cause organ dysfunction Depleted ATP, phosphate, creatine kinase, myoglobin and potassium contribute to the cramping seen and the muscle damage thereafter. The factor causing fatality is the rapid rise of body temperature that accompanies accelerated oxidative phosphorylation for contraction and sequestration of Ca 2+ by sarco/endoplasmic reticulum ATP-ase, such that it surpasses the body’s ability to compensate. The mutation leads to an increased sensitivity of the receptor to any potential agonist resulting in an exaggerated release of calcium resulting in what is known as a hypermetabolic crisis – a rapid acceleration of muscle metabolism with massive consumption of oxygen. Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is an acute condition that arises as a result in the mutation of the ryanodine receptor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the muscle. Adhesion to the surface is energy dependent and so we see ribosomes detach in hypoxic cell injury when ATP/GTP synthesis is reduced.Ĭlinical Relevance – Malignant Hyperthermia Incorrectly folded proteins are kept within the cell and eventually destroyed.ĭespite the presence of ribosomes being such a defining feature of RER, RER-ribosomal interactions are not permanent and thus go through periods of attachment and detachment depending on the demand for protein secretion. Correctly folded proteins are transported to the golgi for secretion. Part of the modification process involves the folding of developing proteins.
Smooth er series#
Proteins that move across the membrane of the RER undergo a series of post-translational modifications, including the addition of signal sequences to target them to the correct part of the cell. The RER takes developing proteins from the cytosol and continues their development prior to completion in the golgi apparatus. In the absence of these cellular mechanisms the cell would probably die.The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) takes its name from the many ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic surface. Without ER in the skeletal muscle fibers couldn't happen muscle contraction. The smooth ER has an important role in lipid and steroid synthesis, it is a storage for intracellular calcium as well. What happens if a cell doesn't have a smooth ER? These units are situated in the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance inside a cell, and are sometimes connected to a unit of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
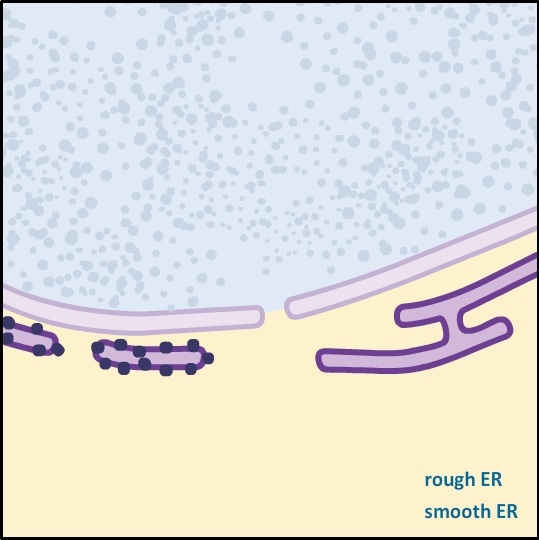
The Structure of Smooth ER The number of smooth ER units in a cell depends on the type of cell and what its manufacturing needs are. One may also ask, where is the smooth ER located? Raw materials go into the cell or a factory to produce goods, and the goods depend on the type of cell. The information in the case of a cell is messenger RNA. Secondly, what is an analogy for smooth endoplasmic reticulum? An analogy for smooth endoplasmic reticulum are the halls of a factory through which information passes. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), meshwork of fine disklike tubular membrane vesicles, part of a continuous membrane organelle within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, that is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids, including cholesterol and phospholipids, which are used in the production of new cellular In this manner, what is smooth ER made of? Smooth ER (SER) acts as a storage organelle. Rough ER is called rough because it has ribosomes attached to its surface. Rough ER looks like sheets or disks of bumpy membranes while smooth ER looks more like tubes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
